Imagine an artificial limb that not only moves in perfect sync with your thoughts but also lets you feel the warmth of a coffee cup or the texture of your child’s hand. This vision is becoming a reality thanks to advancements in sensory feedback technology. Sensory feedback in prosthetics bridges the gap between artificial and biological limbs, enabling users to experience sensations that were once thought impossible to replicate.
As the demand for more intuitive and life-like prosthetics grows, researchers and manufacturers are racing to develop innovative solutions that restore touch, temperature, and even pain perception. This article explores the groundbreaking advancements in sensory feedback technology and how they are shaping the future of artificial limbs.
Understanding Sensory Feedback in Prosthetics
Sensory feedback in prosthetics refers to the ability of an artificial limb to transmit sensory information to the user. This can include touch, pressure, temperature, and even pain—signals that help people interact with their environment.
Unlike traditional prosthetics, which focus solely on movement, sensory-enabled prosthetics aim to replicate the experience of having a natural limb.
Why Sensory Feedback Matters
For individuals with limb loss, the absence of sensory input can create challenges beyond mobility. Without feedback, tasks like gripping an object, applying the right amount of force, or navigating uneven surfaces become difficult.
Sensory feedback addresses these issues by providing real-time information that improves control, reduces mental strain, and enhances the overall experience of using a prosthetic.
For businesses, the integration of sensory feedback represents a significant leap forward. By offering solutions that are both functional and intuitive, manufacturers can cater to a growing market of users seeking prosthetics that feel like natural extensions of their bodies.
The Science Behind Sensory Feedback
Sensory feedback systems rely on a combination of hardware and software to transmit signals between the prosthetic and the user’s nervous system. These technologies are designed to simulate the way biological limbs send sensory information to the brain.
Neural Interfaces and Nerve Stimulation
Neural interfaces are the cornerstone of advanced sensory feedback systems. These interfaces connect the prosthetic directly to the user’s nervous system, allowing for bidirectional communication. When the prosthetic touches an object, sensors on the device send electrical signals to the nerves, mimicking the sensation of touch.
This process often involves electrodes implanted near the residual nerves in the user’s limb. These electrodes deliver precise electrical pulses, stimulating the nerves in a way that the brain interprets as sensory input. Over time, the brain adapts to this stimulation, creating a more natural and seamless experience.
Businesses investing in neural interface technology must prioritize safety, reliability, and user comfort. Collaborating with neuroscientists and medical professionals ensures that these systems meet rigorous standards and deliver consistent performance.

Advanced Sensors
At the heart of sensory-enabled prosthetics are advanced sensors that detect external stimuli. These sensors measure variables like pressure, temperature, and texture, converting them into digital signals that can be processed by the prosthetic’s control system.
For example, piezoelectric sensors can detect minute changes in pressure, allowing users to grip objects with precision. Similarly, thermosensors enable users to sense heat or cold, enhancing their ability to navigate everyday environments.
Businesses developing sensory prosthetics should focus on miniaturization and durability. Compact, robust sensors ensure that the prosthetic remains lightweight and functional under real-world conditions.
Current Innovations in Sensory Feedback
Recent advancements in sensory feedback technology are transforming prosthetics into highly intuitive tools that improve quality of life. From replicating touch to enhancing motion control, these innovations are pushing the boundaries of what artificial limbs can achieve.
Virtual Touch Systems
Virtual touch systems use vibrations to simulate tactile sensations. These systems are especially useful for users who may not yet have access to invasive neural interfaces.
By placing vibrotactile pads on the skin, the prosthetic can transmit sensations like texture or pressure through subtle vibrations.
This non-invasive approach is gaining traction as an accessible and affordable option for enhancing sensory feedback. For businesses, virtual touch systems represent a scalable solution that can reach a broader audience while still delivering significant benefits.
AI-Powered Feedback Loops
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing a pivotal role in advancing sensory feedback. AI algorithms analyze input from the prosthetic’s sensors and refine the feedback delivered to the user. For instance, an AI system can learn a user’s preferences over time, tailoring sensations to feel more natural and intuitive.
Businesses that incorporate AI into their sensory prosthetics can offer products that adapt to individual users, improving satisfaction and usability. Additionally, AI-enabled devices create opportunities for data collection, which can inform future product improvements.
Expanding the Possibilities of Sensory Feedback
Sensory feedback is not just about replicating touch; it’s about creating a seamless connection between the user and their environment. As research advances, new possibilities are emerging that promise to make prosthetic limbs even more intuitive, adaptive, and life-like.
Restoring Complex Sensations
One of the most exciting developments in sensory feedback is the ability to restore complex sensations. Beyond basic touch, researchers are working on systems that enable users to feel texture, temperature, and even pain.
While pain may seem counterintuitive, it plays a crucial role in warning the body about potential harm, such as excessive force or exposure to extreme heat.
For instance, a prosthetic hand equipped with texture-sensing technology could allow a user to distinguish between rough and smooth surfaces.

This capability enhances precision in tasks like writing or handling delicate objects. Similarly, temperature sensors enable users to detect hot or cold environments, reducing the risk of accidental injury.
Businesses exploring these advanced capabilities must ensure that the feedback is both accurate and comfortable. Balancing realism with user preferences is essential to creating a product that feels natural while remaining practical.
Enhancing Mobility with Real-Time Feedback
For lower-limb prosthetics, sensory feedback is instrumental in improving mobility and balance. Systems that provide real-time feedback about ground conditions allow users to adjust their gait instinctively, making walking on uneven surfaces safer and more efficient.
For example, pressure sensors embedded in the foot of a prosthetic leg can transmit signals that mimic the sensation of weight distribution. This information helps users maintain stability, whether they’re walking on a sandy beach or climbing stairs.
Businesses that integrate these systems into their designs can differentiate themselves by addressing a critical user need: confidence in movement. Partnering with biomechanics researchers and physical therapists ensures that these solutions are both scientifically sound and user-friendly.
The User-Centric Benefits of Sensory Feedback
Sensory feedback does more than enhance functionality; it transforms how users interact with their prosthetics and their world. For businesses, understanding these benefits is key to creating products that resonate deeply with users.
Improving Emotional Connection
Prosthetics equipped with sensory feedback help users feel more connected to their devices, fostering a sense of ownership and confidence. When a prosthetic can replicate the sensation of touch, it stops feeling like a tool and starts feeling like an extension of the body.
For example, a user who can feel the grip of their prosthetic hand while holding a loved one’s hand experiences an emotional connection that goes beyond functionality.
Businesses can emphasize these transformative experiences in their marketing, highlighting the human impact of sensory technology.
Reducing Cognitive Load
Traditional prosthetics often require significant mental effort to operate, as users must rely on visual cues and muscle memory to control movements. Sensory feedback reduces this cognitive load by providing intuitive signals that guide the user’s actions.
For instance, a prosthetic hand that vibrates when it grips an object too tightly helps the user adjust their force without needing to constantly monitor the task visually. This frees up mental bandwidth, allowing users to focus on their activities rather than their device.
For businesses, demonstrating how sensory feedback simplifies daily tasks can be a powerful selling point. Highlighting user stories that showcase these benefits helps build trust and engagement with potential customers.
Strategic Opportunities for Businesses
The growing interest in sensory feedback presents a wealth of opportunities for businesses to innovate and lead in the prosthetics market. By focusing on research, collaboration, and user-centric design, companies can create products that stand out while addressing real-world needs.
Investing in Research and Development
Sensory feedback technology is still evolving, making research and development a critical priority for businesses. Collaborating with universities, neuroscience labs, and tech companies can accelerate advancements while providing access to cutting-edge knowledge and resources.
For example, joint research projects focused on non-invasive neural interfaces or advanced sensor materials can yield breakthroughs that set a company apart from competitors. Establishing R&D hubs or innovation labs dedicated to sensory prosthetics ensures that businesses stay ahead of industry trends.

Prioritizing Accessibility
One challenge in sensory prosthetics is ensuring that these advanced devices remain accessible to a wide audience. High costs can limit adoption, particularly in regions with limited healthcare resources.
Businesses can address this by exploring cost-effective manufacturing methods, such as 3D printing, and designing modular systems that allow users to upgrade their devices incrementally.
Partnering with non-profits and government programs to subsidize costs further expands access while demonstrating a commitment to social impact.
Investing in Research for Precision and Performance
Research and development are the lifeblood of innovation in sensory prosthetics. For businesses, dedicating resources to understanding the intricacies of human sensory systems and refining technology to replicate them is essential. Precision and performance are critical metrics for success, especially in competitive markets.
Partnering with universities, neuroscience institutes, and tech companies can provide access to groundbreaking research and insights. These collaborations allow businesses to develop proprietary solutions that set their products apart.
For example, focusing on refining neural interface technologies can lead to prosthetics that provide more natural and accurate sensory experiences, creating a significant competitive advantage.
Building Scalable Manufacturing Pipelines
The demand for sensory-enabled prosthetics is growing, but scalability remains a challenge for many businesses. Advanced technologies like neural interfaces and high-precision sensors often require specialized manufacturing processes that can drive up costs.
To address this, businesses should invest in scalable manufacturing techniques that maintain quality while reducing costs. For instance, adopting automation in the assembly of prosthetics or utilizing 3D printing for components can streamline production without compromising performance.
Creating modular prosthetics is another avenue for scalability. By designing devices with interchangeable components, businesses can simplify production and offer customers the flexibility to upgrade their prosthetic’s sensory features as technology evolves.
Enhancing Accessibility Through Affordability
High-tech sensory prosthetics often come with a price tag that places them out of reach for many users. For businesses, affordability is not just a challenge—it’s an opportunity to differentiate and expand their market.
Offering tiered product lines, where users can choose between basic, mid-range, and premium sensory features, allows businesses to cater to diverse economic demographics. Entry-level devices can focus on essential functions, while high-end models incorporate advanced sensory feedback and customization options.
Collaborations with non-profits, healthcare providers, and insurance companies can further enhance accessibility. Businesses that engage in programs to subsidize costs or offer financing plans demonstrate a commitment to inclusivity, building trust and expanding their customer base.
Leveraging Data for Continuous Improvement
Sensory prosthetics generate vast amounts of data, from user interactions to device performance metrics. For businesses, this data is a goldmine for innovation and improvement.
By analyzing how users interact with sensory feedback features, companies can identify areas for enhancement, such as refining pressure sensitivity or improving response times. Machine learning algorithms can process this data to create smarter, more adaptive prosthetics that evolve with user needs.
Establishing feedback loops, where users can share their experiences and suggest improvements, creates a collaborative environment for product development. Businesses that actively involve users in refining their products gain valuable insights and foster a sense of community and loyalty.

Creating Ecosystems Around Sensory Prosthetics
The future of sensory prosthetics extends beyond the devices themselves. Businesses have the opportunity to build ecosystems that support and enhance the user experience.
For example, companion mobile apps can allow users to fine-tune sensory settings, monitor battery life, or access tutorials. These apps can also serve as a platform for firmware updates, ensuring that prosthetics remain up-to-date with the latest advancements.
Integration with wearable devices, such as smartwatches or fitness trackers, adds another layer of functionality. For instance, a smartwatch could display real-time feedback from the prosthetic, helping users track activity levels or customize responses for different environments.
Expanding Brand Visibility Through Advocacy
The narrative of sensory prosthetics is deeply personal, filled with stories of resilience, empowerment, and transformation. Businesses can harness this narrative to build brand visibility and foster emotional connections with their audience.
Partnering with users to share their experiences—through blogs, videos, or social media campaigns—humanizes the technology and highlights its real-world impact.
Hosting events, such as workshops or panel discussions, provides platforms for advocacy and education, further enhancing the brand’s reputation as a leader in sensory prosthetics.
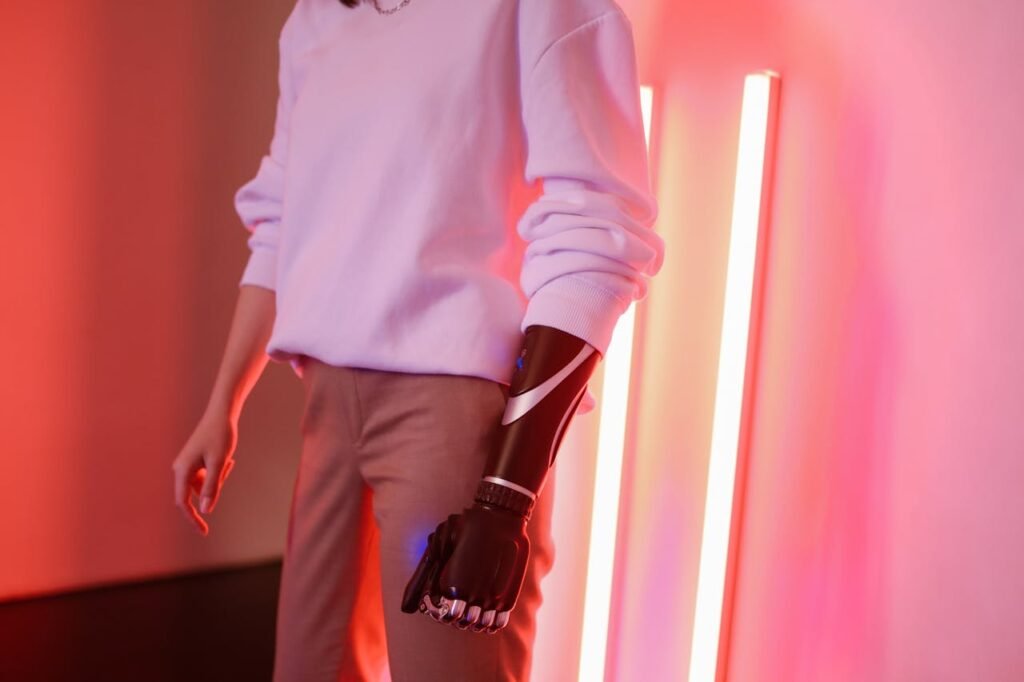

Future Trends in Sensory Feedback for Artificial Limbs
The future of sensory feedback in prosthetics is driven by the convergence of emerging technologies, advanced materials, and a deeper understanding of human physiology. These trends promise to make artificial limbs more intuitive, responsive, and human-like than ever before.
Neural Integration: Bridging the Brain and Prosthetic
Neural integration is at the forefront of sensory feedback advancements. By creating seamless communication between the brain and the prosthetic, these systems aim to mimic the natural flow of information that occurs in biological limbs.
In the near future, neural interfaces could become non-invasive, relying on external devices to capture and transmit brain signals. These innovations would eliminate the need for surgical implantation, making advanced sensory feedback more accessible to users.
For businesses, investing in neural interface research opens doors to groundbreaking products that redefine the user experience. Collaborating with neuroscientists and AI developers is critical to creating systems that are both effective and safe.
Additionally, offering training programs to help users adapt to neural-integrated prosthetics can enhance satisfaction and retention.
Biomimetic Materials for Enhanced Realism
Biomimetic materials—those that mimic the properties of natural tissues—are poised to revolutionize sensory prosthetics. These materials can replicate the elasticity, texture, and sensitivity of human skin, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics.
For example, prosthetic covers made from biomimetic materials can incorporate embedded sensors that detect touch, temperature, and pressure. These covers not only improve the sensory experience but also provide a more life-like appearance, boosting users’ confidence in social settings.
Businesses can lead this trend by partnering with material scientists to develop and test biomimetic solutions. Highlighting these features in marketing efforts emphasizes the advanced and human-centered nature of the product, appealing to users who value both form and function.
AI-Driven Personalization
Artificial intelligence will play an increasingly important role in tailoring sensory feedback to individual users. Advanced AI systems can learn a user’s unique preferences, adjusting feedback intensity and types of sensations to suit their needs.
For instance, an AI-powered prosthetic could recognize that a user prefers softer tactile sensations when gripping fragile objects but firmer feedback for high-pressure tasks. Over time, the system refines its responses, creating a highly personalized and intuitive experience.
Businesses can leverage AI to differentiate their products and offer features that adapt over time. Building proprietary AI platforms or integrating with existing systems allows companies to enhance their devices’ performance while fostering long-term user loyalty.
Strategies for Businesses in Sensory Prosthetics
The evolution of sensory feedback technology creates new opportunities for businesses to lead, innovate, and grow. Strategic approaches that prioritize user needs, technological advancements, and sustainability can set companies apart in the competitive prosthetics market.
Creating Scalable Solutions
One challenge in sensory feedback technology is balancing sophistication with scalability. High-tech prosthetics often involve complex systems that can be cost-prohibitive to produce and maintain. Businesses should focus on designing scalable solutions that maintain quality while reaching a larger audience.
For example, modular sensory prosthetics allow users to upgrade features incrementally, such as adding advanced sensors or AI capabilities when they become affordable. This approach expands accessibility while building a foundation for long-term customer relationships.
Building User-Centric Support Ecosystems
A prosthetic device is only as effective as the support system behind it. Businesses can enhance the user experience by creating ecosystems that provide resources, education, and connectivity.
For instance, companion mobile apps can allow users to monitor and adjust sensory feedback settings, access tutorials, and communicate with customer support. Online communities where users share tips and experiences foster a sense of belonging and help new users adapt more quickly.
By investing in user-centric support, businesses build trust and demonstrate a commitment to improving the lives of their customers.
Emphasizing Sustainability
As the demand for advanced prosthetics grows, sustainability is becoming an important consideration. Businesses that prioritize eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient technologies not only reduce their environmental impact but also appeal to socially conscious consumers.
For example, prosthetics that incorporate recyclable components or renewable energy sources like kinetic charging stand out as innovative and responsible solutions. Communicating these sustainability efforts in marketing campaigns builds goodwill and strengthens brand reputation.
Conclusion
The future of sensory feedback in artificial limbs is nothing short of revolutionary. From restoring the sense of touch to enabling users to navigate their environments with unprecedented precision, these advancements are transforming how prosthetics are designed and experienced. Sensory feedback bridges the gap between artificial and biological, allowing prosthetics to feel like natural extensions of the body.
For businesses, this field presents an incredible opportunity to innovate, impact lives, and lead in a rapidly evolving industry. By focusing on user-centered solutions, exploring cutting-edge technologies, and prioritizing accessibility, companies can create prosthetics that are not only functional but also life-changing.
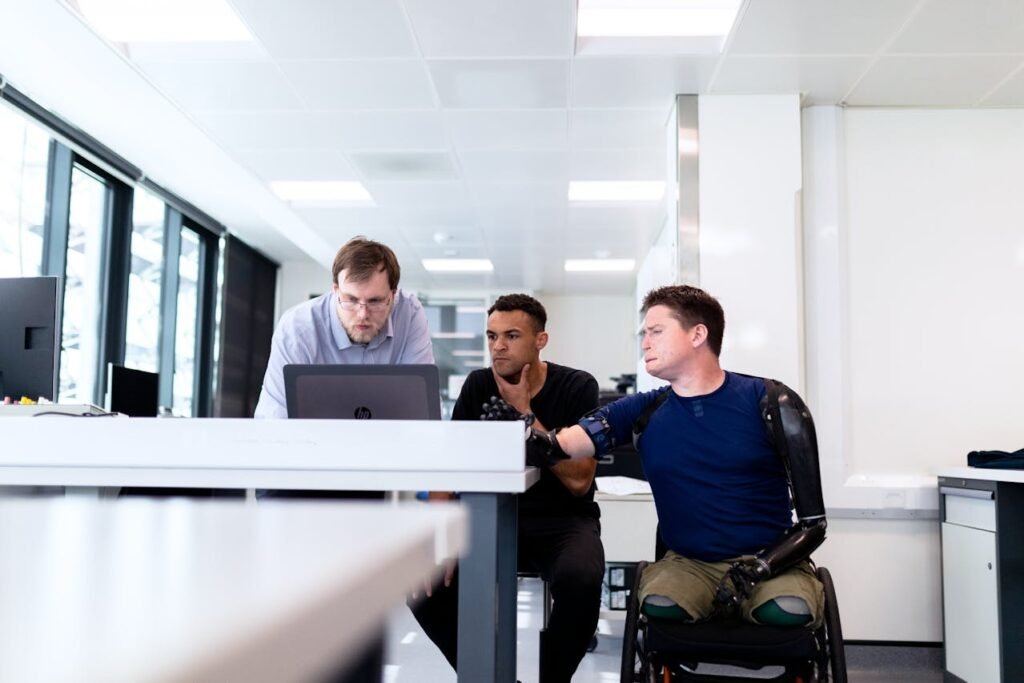




Pingback: Discover the Amazing Capabilities of Artificial Hands – Prosthetics Blog